The following is the latest updates on resumed fighting in Gaza Strip:
Hamas says Israel, US responsible for truce expiration:
Hamas top official Osama Hamdan said the “responsibility for not extending the ceasefire lies with the Zionist regime and the United States”.

He said the Palestinian resistance was seriously looking for a ceasefire and is still pursuing it.
Gaza death toll in few hours rises to 36:
The heath ministry spokesperson in Gaza Ashraf al-Qudra confirmed that the death toll had risen to 32 Palestinians.
Qudra said the dead included ten people killed in al-Maghazi in central Gaza, nine in Rafah in the South, and five in Gaza City in the north – hours after the truce ended at 7 a.m. local time (0500 GMT) .
Another journalist martyred in Gaza:
Palestinian sources announced the martyrdom of “Abdullah Darwish”, a photographer and reporter of the “Al-Aqsa” satellite channel after the resumption attacks by the Zionist regime on the Gaza Strip. So far, as many as 71 reporters have been killed in the Israeli regime airstrikes.

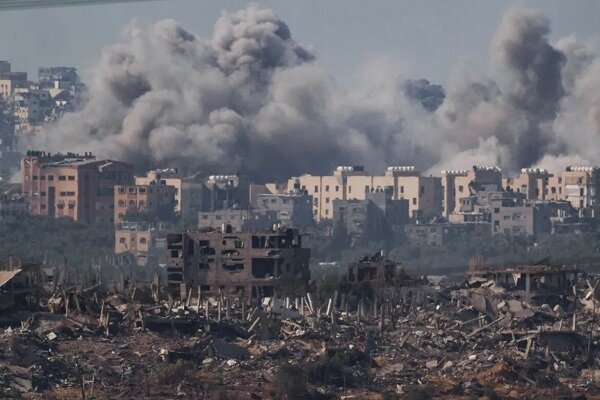
Six killed in Rafah strike, as explosions heard across Gaza:
In the resumed airstrikes by the Zionist regime on different areas of Gaza, 6 people were martyred and dozens were injured.
Israeli regime airstrikes have hit southern Gaza, including the community of Abassan east of the town of Khan Younis, Hamas officials say. Another strike hit a home northwest of Gaza City.
Loud, continuous explosions are heard coming from the Gaza Strip, and black smoke billows from the territory.
The Gaza health ministry says three people have been killed in Israeli air raids in Rafah, in the Strip’s south.
Israeli military says resumed fighting in Gaza
The Israeli regime army has issued a statement saying that it has resumed its military campaign in the Gaza Strip, claiming that Hamas violated the truce by firing into occupied territory.
International mediators, including Qatar, Egypt and the US, were on Friday pushing for another extension of the Gaza truce ahead of its expiration at 7am local time (05:00 GMT), Al Jazeera reported.
With no extension announced by the deadline, there were reports of gunfire and explosions in the north of the Gaza Strip, while the Zionist regime’s military said it had intercepted a rocket from Gaza.
An AFP journalist reported Israeli airstrikes, artillery fire seen in Gaza City the Zionist regime media said.
Photos on social media claim to show a recent strike,
Meanwhile, Lebanese Al-Mayadeen network reported fighting between the Palestinian resistance fighters and the Zionist regime military in the northwest of Gaza.
Fierce clashes were going on between the Resistance fighters and the occupying Israeli forces in the northwest of Gaza, Al-Mayadeen said.
According to the report, Resistance fighters confronted the tanks of the Zionist regime in that area.
The temporary ceasefire between Hamas and the Zionist regime ended today as deadline passed.
The Palestinian Islamic Resistance Movement, Hamas, launched an operation against the Zionist Israeli regime on October 7 in response to more than seven decades of occupation of Palestine and nearly two decades of blockade of Gaza and imprisonment and torture of thousands of Palestinians. It killed more than 1,200 Zionists soldiers and settlers and took more than 220 of them to the enclave as prisoners.
In retaliation to Hamas’s operation, which was called the al-Aqsa Storm operation, the Zionist regime launched heavy attacks against Gaza and put the enclave under total siege.
More than 15,000 Palestinians have been killed in the Zionist regime’s attacks, while tens of thousands of others have been injured.
MNA